THIS WEBSITE IS UNDER CONSTRUCTION. PLEASE CHECK BACK SOON.
Pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension is a disease that is caused by high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries. Pulmonary hypertension is defined as pulmonary artery mean pressure ≥ 25 mm Hg at rest. Prolonged and untreated high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries leads to deterioration of right ventricular work. This may manifest feelings of lack of air (dyspnea), chest pain, swelling of extremities, loss of appetite, weakness, dizziness and fainting states.
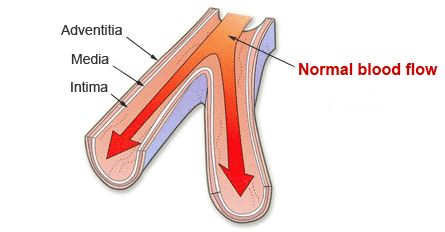
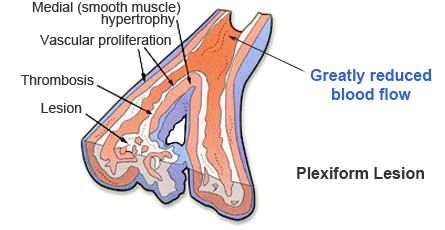
Pulmonary hypertension affects small pulmonary arteries. The first picture shows a healthy pulmonary artery with normal blood flow. The next picture shows a gradual thickening of the muscle cell walls, which leads to its narrowing, increased pressure in the pulmonary arteries and reducing blood flow.
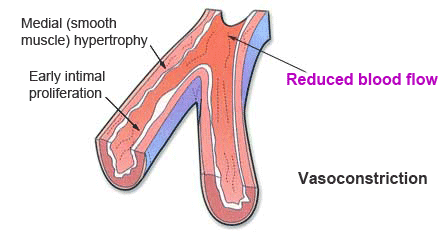
Higher pressure in the pulmonary arteries is causing further muscle hypertrophy. Over time in these places can develop blood clots.